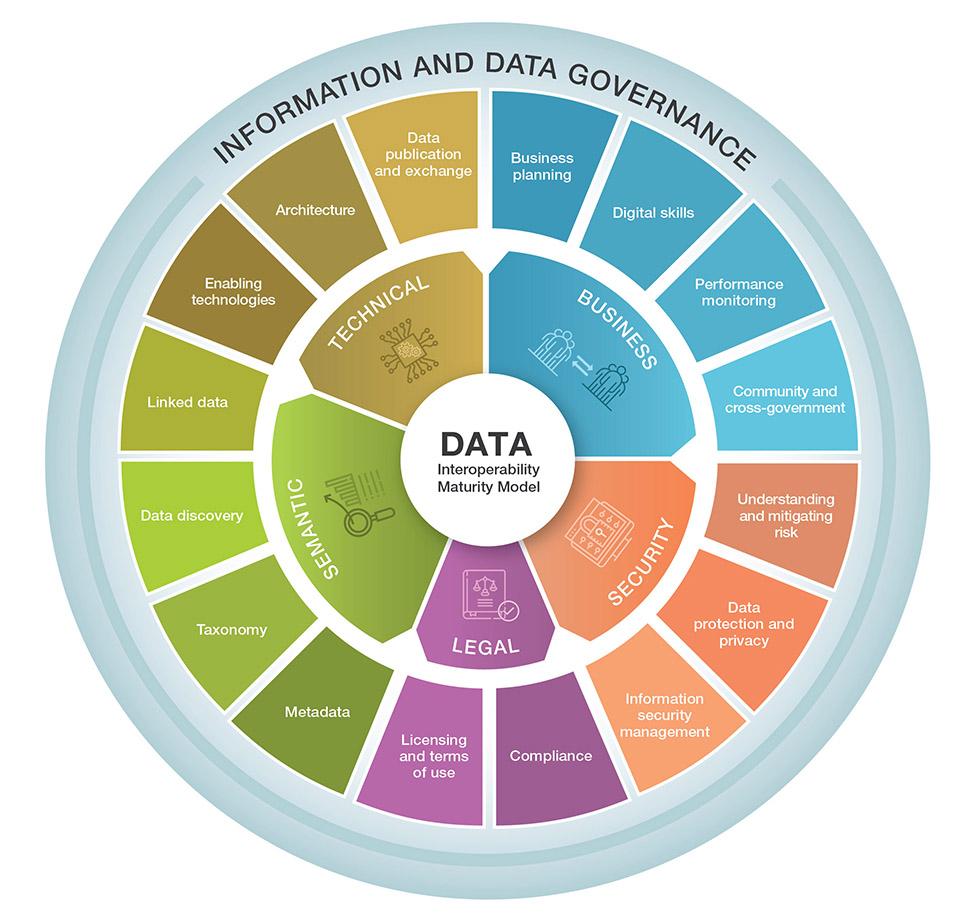
The DIMM helps you measure your agency’s progression across 5 interoperability key themes and assess your agency's information and data governance (which coordinates and drives delivery across these themes).
- Business: operational maturity for producing, consuming and sharing data on a tactical level
- Security: awareness of, and response to, the security risks and issues of data interoperability
- Legal: legal support for data interoperability
- Semantic: the data structures that enable the meaning of exchanged information to be understood by people and systems
- Technical: the technology that supports data interoperability, including computer systems and services
Each area is split into categories. Each category has 5 steps that describe the common data interoperability behaviours, events and processes for the corresponding level of maturity. The steps are:
- initial
- developing
- defined
- managing
- optimising
Using the DIMM
The DIMM can be used by people at every level of your organisation, from information management professionals working in data governance or analytics to senior leadership teams setting agency targets and strategies.
It can be applied to all data produced by your agency that have the potential to be integrated, exchanged or shared.
The DIMM is not a prescriptive standard and does not measure how open your data is or how much data you share.
You can use a DIMM assessment to:
- self-evaluate your current level of data interoperability maturity
- identify gaps in data interoperability maturity
- plan improvements to reach the level of maturity your agency needs
What does success look like?
Your agency is using the DIMM successfully when it:
- has plans in place to build data interoperability maturity to each ‘defined’ step or higher. This could be assisted by a strategy, roadmap or plan
- monitors data interoperability over time to make further improvements that align with business needs
Your agency does not need to be at the ‘optimising’ step to have effective data interoperability.
Performing a DIMM assessment
There are 4 stages to using the DIMM to assess your current level of maturity and make plans to improve it.
Start your assessment by downloading the DIMM assessment tool (PDF, 409kB).
1. Conduct a scope assessment
Define your key participants and assessment parameters.
Who are the key stakeholders that need to be involved in the assessment?
Are you assessing interoperability maturity for the whole agency, a division, a branch, a program or a single project?
2. Assess the current state
Using the DIMM assessment tool (PDF, 422kB), talk to subject matter experts and stakeholders to identify and document your current level of maturity (step) for each category. This is your baseline maturity.
To choose a level of maturity, you must also meet the characteristics and behaviours of all lower levels. For example, you should only select the 'optimising' step if you already meet the behaviours in the 'managing' step.
Your level of maturity can vary between categories.
3. Identify the desired future state
Talk to key stakeholders about the level of maturity you need to meet your short and long-term business needs.
Document your desired future state for each category, noting that it can vary between categories and be different to other agencies'.
For each category, compare your baseline maturity to your desired future state and document any gaps in data interoperability maturity.
4. Plan for change
Analyse your results to confirm your agency's current strengths and document areas for improvement.
You can use the results to inform strategic planning and investment activities or to create a roadmap for improvement. We recommend plotting a path that leads from your baseline to your target maturity for each category.
Repeat the assessment to track data interoperability improvements and trends over time.
Get in touch with us
We welcome your feedback about the usability and content of the DIMM. Please contact the Agency Service Centre with any comments or questions.